What Is OpenVPN? A Guide to the VPN Protocol in 2025
- Table of Contents
- What Is OpenVPN?
- OpenVPN: How It Works
- What Is OpenVPN Used For?
- OpenVPN UDP vs OpenVPN TCP
- OpenVPN vs Other Protocols: Which Is Best?
- OpenVPN Benefits & Challenges
- Is OpenVPN Safe, Secure & Private?
- Can I Use OpenVPN for Free?
- What Are the Best VPNs That Use the OpenVPN Protocol?
- Conclusion
- FAQ: OpenVPN Explained
Quick Summary: What Is OpenVPN?
OpenVPN is a secure and versatile VPN protocol used in popular VPN services like ExpressVPN, NordVPN and Surfshark. It offers flexible configurations and strong community support, making it a reliable choice for secure online connections.
OpenVPN is a widely used VPN protocol known for its security and versatility. If you have ever set up a connection on your device to one of the best VPNs, there is a high chance that you have come across it. If you’re still confused, follow along as I answer the question, “What is OpenVPN?”
For those new to VPN technology, a VPN protocol, also called a tunneling protocol, is a set of rules and specifications that govern how data is encrypted and transmitted between your device and the VPN server. See our “What Is a VPN?” article if you haven’t heard of this privacy technology.
Each VPN protocol employs its own set of rules and technologies, so privacy, security and internet speeds vary from one protocol to another. In this article, I will discuss everything you should know about what OpenVPN is, how it works, how it stacks up against other VPN protocols and much more.
What Is OpenVPN?
The OpenVPN tunneling protocol is an open-source protocol used in many popular virtual private network (VPN) solutions, including ExpressVPN, NordVPN and Surfshark. A VPN protocol is a set of rules that creates an encrypted tunnel between your device and your VPN server, ensuring the two can communicate without being configured beforehand.
Is OpenVPN a VPN?
No, OpenVPN is not an out-of-the-box VPN service like ExpressVPN or NordVPN. It’s a secure VPN protocol that you can activate in your VPN client settings. OpenVPN software, which is open-source and free to download, allows you to create your own VPN and connect to any OpenVPN server.
OpenVPN: How It Works
OpenVPN uses advanced encryption techniques to secure your internet connection. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how it works.
Authentication Methods
Before connecting your device to a VPN server, OpenVPN authenticates the identities of both your device and the server. In a typical credential-based authentication process, the VPN server verifies your username and password before allowing the connection. A digital certificate-based authentication process uses digital certificates to verify your device and the VPN server.
Other authentication methods OpenVPN can use include pre-shared keys and public key infrastructure (PKI) handled by RSA — a public-key cryptosystem.
Client-Server Tunnel
Once OpenVPN has verified the trustworthiness of the VPN client (that’s you, the user) and the VPN server, it creates an encrypted tunnel using Secure Sockets Layer/Transport Layer Security (SSL/TLS) as its security protocol.
Data Encryption
After the tunnel is established, OpenVPN encapsulates data packets by adding routing and security information layers. Then, OpenVPN encrypts data packets using the OpenSSL library.
OpenVPN allows customization of encryption methods, supporting various cryptographic algorithms and key lengths to meet different security needs. Most VPN clients build a custom security protocol that uses AES-256-GCM for encryption.
Data Transmission to a VPN Server
Once OpenVPN has encapsulated and encrypted your data, it transmits it to the VPN server through the established tunnel. When it reaches the server, your data is decrypted and sent to its intended destination. This process hides your IP address, making only the VPN server’s IP visible to the outside world so you can circumvent surveillance or get Netflix unblocked.
What Is OpenVPN Used For?
OpenVPN is used to secure connections and protect data. The following are key OpenVPN use cases:
- Setting up a VPN connection: The OpenVPN protocol is widely used to create an encrypted tunnel from a device to a server owned by a VPN provider.
- Encrypting data within a tunnel: Besides creating an encrypted tunnel from a device to a VPN server, OpenVPN also encrypts data that passes through the tunnel.
- Creating secure remote access: OpenVPN provides a secure way for remote employees to access corporate networks by setting up encrypted tunnels and protecting data in transit.
- Joining multiple sites: Companies can use OpenVPN to establish site-to-site VPN connections, securely linking multiple sites, data centers or networks to share resources safely.
OpenVPN UDP vs OpenVPN TCP
The OpenVPN protocol can operate over two transmission protocols: User Datagram Protocol (UDP) and Transmission Control Protocol (TCP). All the best VPNs on the market allow you to select either UDP or TCP for your VPN connection.
The OpenVPN UDP protocol sends data in a stream without establishing a permanent connection. It still must authenticate the destination server, but it doesn’t build a permanent channel like TCP does. This approach allows for faster data transmission, as it bypasses the need for handshakes or acknowledgments between the sender and receiver.
However, it also means that if packets are lost or arrive out of order, they won’t be automatically retransmitted, thus affecting the transport protocol’s reliability in unstable network conditions.
OpenVPN TCP establishes a connection through a handshake before data transmission begins. It guarantees reliable, error-free packet delivery and retransmits lost packets. However, its acknowledgment and error correction processes introduce delays, making it slower than OpenVPN UDP.
Both OpenVPN UDP and TCP are perfect for obfuscation — the practice of disguising VPN traffic to make it less detectable by firewalls or network-monitoring systems.
| TCP | UDP |
|---|---|
| High reliability due to packet retransmission | Lower reliability; no retransmission of lost packets |
| Sequential packet delivery, making it ideal for email, web browsing and other static uses | Packets moved in a stream, making it suitable for streaming, gaming, VoIP and other dynamic uses |
| Waits until buffer space is available before sending packets | No flow control |
| Lower speed due to packet retransmission overhead | Higher speed due to no-overhead packet retransmission |
OpenVPN vs Other Protocols: Which Is Best?
OpenVPN excels at compatibility. It supports a wide range of devices and routers, and offers strong security and fast speeds.
WireGuard, a newer protocol, offers superior speeds and security compared to OpenVPN thanks to its faster authentication and lean codebase. However, it doesn’t support as many operating systems and devices as OpenVPN. IKEv2/IPsec may be a better choice for mobile devices because of its auto-reconnect feature, speed and stability.
The best protocol depends on how you want to use the VPN. To provide optimum VPN benefits, all leading VPN providers have an auto-connect protocol feature that helps you pick the fastest available VPN protocol for your chosen VPN server.
Here’s a quick comparison of different types of VPN protocols and how they stack up against each other.
| Protocol: | Security | Speed | Encryption |
|---|---|---|---|
| OpenVPN | High | Fast | AES-256 |
| WireGuard | High | Fast | ChaCha20 |
| L2TP | High | Good | AES-256, 3DES |
| PPTP | Weak | Fast | MPPE |
| IKEv2 | Good | Fast | AES-256, 3DES |
| Shadowsocks | Average | Fast | AEAD_CHACHA20_POLY1305, AEAD_AES_256_GCM |
| SSTP | Average | Average | AES-256 |
OpenVPN Benefits & Challenges
OpenVPN is a reliable VPN protocol. It offers good security, excellent flexibility and the possibility of obfuscation, but it’s reasonable to consider the pros and cons before making it your default VPN protocol.
- Diverse connection modes (point-to-point or site-to-site)
- Supports strongest available encryption, including AES-256
- Stable connections
- Open-source
- Can consume more battery power
- Speeds can be lower than WireGuard and IKEv2
- Potential for configuration errors if not using a commercial VPN
- Complex configuration if you don’t use a commercial VPN like ExpressVPN
Is OpenVPN Safe, Secure & Private?
Yes, the OpenVPN protocol is safe, secure and private. It uses AES 256-bit encryption most often, which modern computers cannot crack. OpenVPN supports perfect forward secrecy, meaning encryption keys are regularly changed. This ensures that hackers can’t decrypt past or future sessions even if they obtain a key.
OpenVPN is also flexible, allowing you to choose between UDP for speed and TCP for stability. Its open-source nature means a large community of OpenVPN developers can review its code, making finding and fixing vulnerabilities easier.
Can I Use OpenVPN for Free?
Yes, you can use OpenVPN for free. If you have technical skills, you can utilize OpenVPN Connect, a free VPN client developed by the OpenVPN company, or employ the OpenVPN Software Community Edition to create your own VPN and access the OpenVPN protocol at no cost.
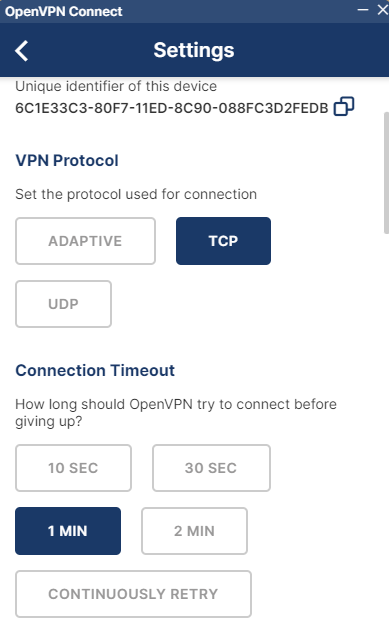
Additionally, you can use OpenVPN Access Server, a commercial product that allows up to two free simultaneous connections without the need for a paid license.
For an average user who wants a simple plug-and-play solution, an easier method is to use free VPN services like PrivadoVPN or Windscribe that support the OpenVPN protocol. However, these free VPNs often limit your choice of server locations and security features and usually have data caps.
What Are the Best VPNs That Use the OpenVPN Protocol?
Most reputable VPNs come with OpenVPN. Here’s a quick overview.
- ExpressVPN — ExpressVPN is my favorite VPN. It comes with fast speeds, RAM-only servers and a threat manager to block ads, trackers and malware. ExpressVPN offers OpenVPN over UDP and TCP, but this prevents you from using advanced threat protection. Read our detailed ExpressVPN review to explore its features more closely.
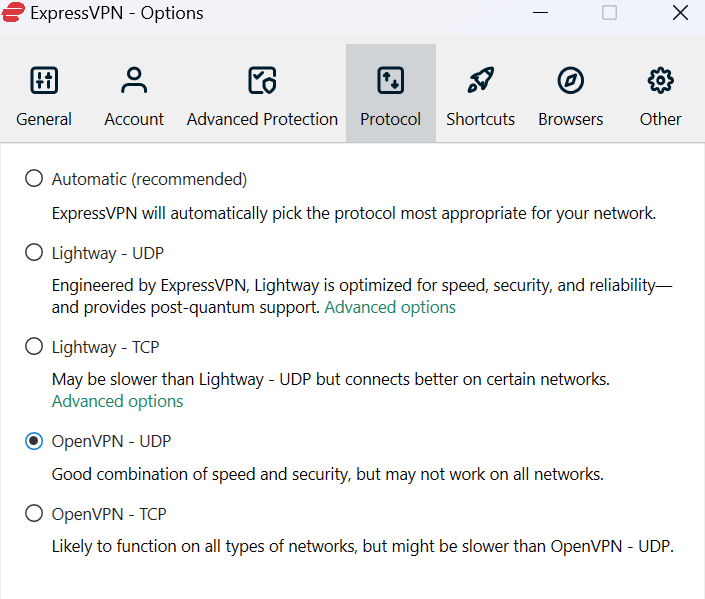
- NordVPN — When writing his NordVPN review, my colleague found that it offers good speeds, a strict zero-logs policy and threat protection features. It also allows you to use UDP or TCP as your VPN protocol, but you need to turn off the “web protection” feature to use these protocols.
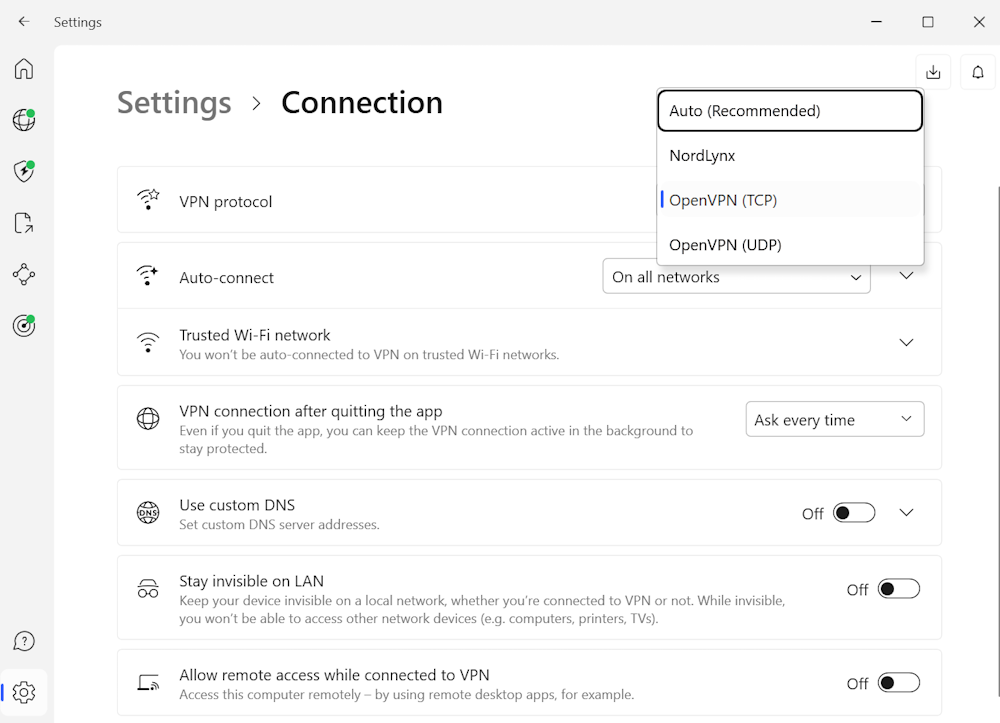
- Surfshark — If you want a cheaper option than ExpressVPN and NordVPN but still want decent speeds and security features, Surfshark is your best bet. It allows you to use OpenVPN UDP or OpenVPN TCP without disabling the ad blocker. Read our detailed Surfshark review to explore its features thoroughly.
Conclusion
OpenVPN’s balance of security, speed and compatibility makes it a top VPN protocol. Remember that the safety of any VPN depends on more than just the protocol, though — it also relies on the provider’s privacy policies and server security.
The PrivacyJournal team has extensively tested ExpressVPN, NordVPN and Surfshark and found them to be perfectly safe when using the OpenVPN protocol.
Do you use OpenVPN? Which VPN protocol is your go-to? I’d love to hear about it in the comments section. Thanks for reading.
FAQ: OpenVPN Explained
What Does OpenVPN Do?
OpenVPN is a virtual private network protocol. When you use OpenVPN as your VPN protocol, several VPN functions rely on it, such as authentication mechanisms, encryption protocols and data transmission processes.What’s the Difference Between a VPN and OpenVPN?
A VPN is a service that masks your IP address and secures your internet connection by encrypting your data. OpenVPN, on the other hand, is a specific protocol that VPNs use to create these secure connections.Is OpenVPN Free?
Yes, OpenVPN is a free, open-source protocol. Many free VPNs use it, such as Proton VPN and Windscribe, making it accessible for free. However, free VPNs come with limitations like restricted data, bandwidth, server options and security features.Is It Safe to Use OpenVPN?
Yes, using the OpenVPN protocol is safe, especially with premium VPNs like ExpressVPN, NordVPN or Surfshark. However, it might be less secure with free VPNs, some of which may sell your data to third parties.

Leave a Reply